The room: E-mail protocols are explained and practice is done with wireshark.
Task 1: Introduction
1.1. What is the MITRE ID for Software Configuration?
MITER ID is available at this link.

M1054
Task 2: SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
2.1. What is the SPF rule to use if you wish to ensure an operator rejects emails without potentially discarding a legitimate email?
SPF publishes a list of servers authorized to send emails to a domain. It makes the most sense to end the SPF record with “and everything else on the Internet is NOT authorized.”
There are two options in the SPF record for this ending;
~all (softfail)
-all (fail)
Deleting a lot number of emails in the SPF records caused the correct emails to be deleted. -all is usually an operator that discards legitimate emails. This can be avoided by using “~all” instead of “-all” to eliminate the problem.
v=spf1 ~all
2.2. What is the meaning of the -all tag?
fail
Task 3: DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
3.1. Which email header shows the status of whether DKIM passed or failed?
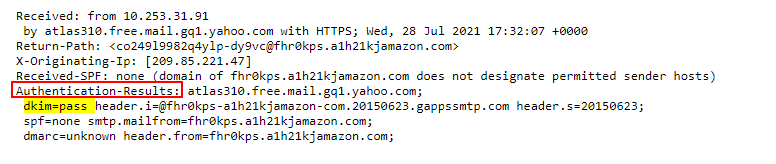
Authentication-Results
Task 4: DMARC (Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
4.1. Which DMARC policy would you use not to accept an email if the message fails the DMARC check?
The DMARC policy is used to determine what to do with incompatible emails:
p=none: is used to collect feedback and gain visibility into email streams without impacting existing flows
p=quarantine: allows email receivers to treat email that fails the DMARC check as suspicious and files them in a SPAM folder.
p=reject: requests that email receivers reject email that fails the DMARC check.
p=reject
Task 5: S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
5.1. What is nonrepudiation? (The answer is a full sentence, including the “.”)
I think such questions are not instructive. It is clear that we are asked to read the source, but most of us copy-paste instead of reading the source.

The uniqueness of a signature prevents the owner of the signature from disowning the signature.
Task 6: SMTP Status Codes
6.1. What Wireshark filter can you use to narrow down the packet output using SMTP status codes?
You can reach the source.
smtp.response.code
6.2. Per the network traffic, what was the message for status code 220? (Do not include the status code (220) in the answer)

<domain> Service ready
6.3. One packet shows a response that an email was blocked using spamhaus.org. What were the packet number and status code? (no spaces in your answer)
We can see the text “Email blocked using spamhaus.org” in the response.

156,553
6.4. Based on the packet from the previous question, what was the message regarding the mailbox?

mailbox name not allowed
6.5. What is the status code that will typically precede a SMTP DATA command?
354
Task 7: SMTP Traffic Analysis
7.1. What port is the SMTP traffic using?

25
7.2. How many packets are specifically SMTP?

512
7.3. What is the source IP address for all the SMTP traffic?

10.12.19.101
7.4. What is the filename of the third file attachment?
To facilitate the solution to this problem, the task has left us a link. Wireshark codes for Internet Message Format (IMF) are available here.


attachment.scr
7.5. How about the last file attachment?


.zip
Task 8: SMTP and C&C Communication
8.1. Per MITRE ATT&CK, which software is associated with using SMTP and POP3 for C2 communications?
Click on the article link.

Zebrocy
Task 9: Conclusion
9.1. Per the playbook, what framework was used for the IR process?
NIST

Hello, I am Aleyna Doğan. I work as a Cyber Threat Intelligence Analyst. In my blog, we write blog posts that my friends and I want to share. Have a good read.







[…] Click for the previous blog post […]
[…] TryHackMe: Phishing Emails 4 Room (Phishing Prevention) Writeup admin […]
[…] TryHackMe: Phishing Emails 4 Room (Phishing Prevention) Writeup admin […]